These are two ligaments that cross each other inside the knee. Their specific function is to restrict the movement of the knee in the anterior and posterior positions and to keep the knee more stable.
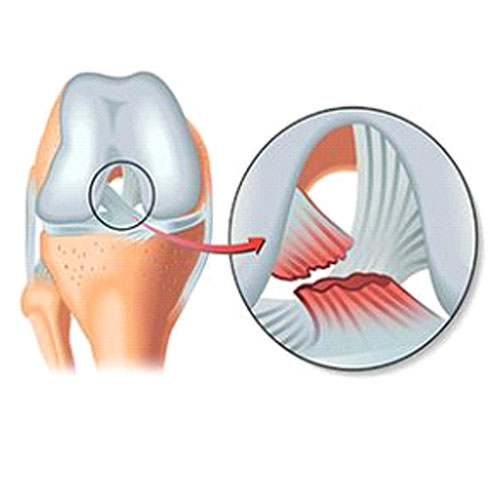
Tears occur especially as a result of blows to the knee and sudden turns of the body while the tibia is fixed. They are especially common in sports such as tennis, soccer and basketball, which require sudden turns and fast movements. Posterior cruciate ligament injuries are often overlooked due to their rarity. A proper physical examination followed by X-rays and MRIs can make the diagnosis.

In people with damaged anterior cruciate and posterior cruciate ligaments, the stability of the knee decreases. This facilitates the formation of meniscus tears, cartilage damage and other ligament damage, and also causes arthritis (arthrosis) in the knee at an early age due to the micro-level anterior-posterior movements of the cartilages of the knee.
In the past, treatment of anterior and posterior cruciate ligament injuries was recommended for young and active athletes. However, studies have shown that patients with anterior cruciate ligament damage develop knee arthritis (gonarthrosis) in the early period… Therefore, it is recommended for all young and middle-aged patients who walk, bend, get up, do daily sports, like to walk, have a mobile lifestyle.
In the surgery, a new ligament is generally created. The new ligament is placed in the anatomical position of the existing ligament by opening special tunnels in the thigh and shin bones. The operation is performed arthroscopically (closed).

Unless there is a very extreme situation in the postoperative period, it is not necessary to use a knee brace and walking with full load can be started the day after the operation. For 15 days, it will be good to use crutches as a precaution. Joint movement at first


